What is network latency and what can you do about it?
Network latency, or lag, is a measure of how long it takes data to transit a network from source to destination. This could be from a server to a desktop, a website to a mobile or an online game server to your computer. Whenever data transits a network, an amount of latency is involved.
The internet is made up of a series of servers providing services, routers that process the traffic and network cable that is used to transport the data. In any given route there could be several network routers and several hundred, or even thousands of miles of cable within that route.
Even though data travels at the speed of light over fibre networks, the distances involved and the number of routers in the path can cause delays, or latency.
Latency is only a measure of the time it takes for that data to pass from the server to your device. It does not take into account the processing time at either end.
Why is network latency an issue?
The rise of cloud services means networking is now more important than ever. Delays can cause frustration and reduce productivity. Cloud apps that rely on synchronization can not work. The more we depend on connected devices, the more latency becomes an issue.
If you use VoiP or other video conferencing technology, latency can cause stuttering and loss. Neither of which make you look very professional.
If you’re a gamer, latency is the enemy. Any lag, even the tiniest delay can mean the difference between a win and a loss. If you’re working from home user a secure VPN, latency can cause connections to slow to a crawl or the authentication server to lose sync and dump you off the network.
How do you measure latency?
You can test network latency from any device but it is easiest from a desktop or laptop. You can perform a simple test from a terminal or tool to give you an idea of where any lag is being caused.
The most basic, but reliable of these tests is Ping. It stands for Packet Internet Groper and is a very simple tool for measuring latency in networks among other things.
In Windows 10:
- Type ‘CMD’ into the Windows Search box and select Command Prompt.
- Type ‘ping www.google.com’ and press Enter.
In MacOS:
- Open Applications and Utilities.
- Select the Network Utility and open the Ping tab.
- Select www.google.com and select Ping to launch the test.
Both should provide a readout of what the ping discovered. You should see a list of replies with the IP address of the server contacted and a time. It is this time that indicated lag or latency.
The time is measured in milliseconds. The higher the number, the longer it took to receive a reply from the server being pinged. This is latency.
Don’t worry if you see entries that time out. Some servers, such as some DNS servers are programmed to ignore pings for security. Request Time Out messages on a single hop are nothing to worry about.
Traceroute
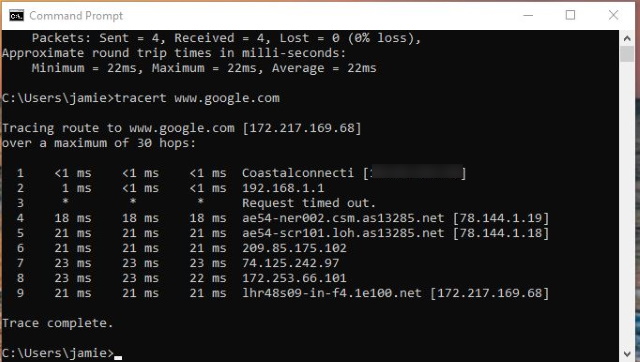
You can also use Traceroute to measure latency. This is a more exacting test of latency and would typically be used if the simple ping test showed lag.
You would repeat the above but switch ‘ping’ for ‘tracert’ in Windows or ‘traceroute -I’ in Mac or Linux. This will provide a much more detailed outline of the route the traffic took from your device to the server and the time it took for it to happen.
Tracert is useful because it can show you exactly where in the route the lag is occurring. For example, if you see most hops are 1ms but then jumps to 55ms on a single hop, it is likely the lag is coming from that part of the network.
Home users won’t be able to do much about that except relax as the delay isn’t down to your computer or home network.
IT support on the other hand may have work to do if the latency is happening within a corporate network or within a defined route.
How to reduce latency
If ping or tracert show latency on your home network or close to home, there are a couple of things you can do about it.
- Reboot your computer to refresh the network layer of your operating system.
- Reboot your router to refresh the IP address and the connection.
- Minimise the number of users online at any one time.
- Switch from WiFi to Ethernet.
- Shut down any applications that use the internet.
- Perform a broadband speed test to identify any issues with your connection.
- Check your DNS server and switch to a new provider.
For home users, the majority of latency issues are outside your control. Many will be down to network congestion, your ISP or the core network. If your broadband connection is typically slower than you would like, contact your ISP as they may be able to help.
FAQs around network latency
What is good network latency?
Good network latency depends on what you’re doing. For gamers, the less latency the better but practically, that means <30-50ms. Cloud applications, video conferencing and voice calls are slightly more forgiving but should not ideally exceed 100ms.
What causes network latency?
For home users, network latency is caused by factors out of your control. Causes include busy ISP networks, oversubscribed game servers, long distances between your computer and the host or even a Distributed Denial of Service attack in progress. Some latency can be caused by home networks but the vast majority are on the core network.
Does faster internet lower ping?
A faster internet does not necessarily lower ping. If you live in a busy household with lots of people online at once, it will certainly help. Many causes of latency happen within the provider or core network so a faster internet connection won’t make any difference.
What is TTL in Ping?
TTL in ping means Time to Live. It is a counter that tells the router handling the ping how long the packet has been there. This is part of traffic management and routers are usually programmed to discard packets that are too old.
Is 0 Ping possible?
No. 0 ping is not possible with current technology. Internet traffic may travel at the speed of light over fibre networks but distance and processing via your computer’s network card, operating system and any routers will inevitably lead to delay.